Is investing young smart?

Investing early offers significant advantages, but also presents unique challenges. This article explores the compelling reasons why starting young can be a smart financial move, despite potential risks.
We'll delve into the power of compounding returns, the benefits of long-term growth, and how to navigate the complexities of investing as a beginner.
From understanding risk tolerance to choosing appropriate investment vehicles, we'll equip young investors with the knowledge to make informed decisions and build a secure financial future.
Is Investing Young Smart? A Deep Dive into Early Investing
Yes, investing young is incredibly smart for a multitude of reasons. The most significant advantage is the power of compound interest. Starting early allows your investments to grow exponentially over a longer period.
Even small, consistent contributions made in your twenties will yield significantly larger returns by retirement age compared to someone who starts investing later. This isn't just about making more money; it's about creating financial security and independence for your future.
Young investors also have a higher risk tolerance, allowing them to potentially benefit from higher-growth investments that may be too risky for someone closer to retirement. Moreover, young people typically have more time to recover from potential market downturns, as they have a longer investment horizon. Finally, starting early fosters a crucial habit of financial discipline and planning, skills valuable throughout life.
The Power of Compound Interest and Time
The earlier you start investing, the more time your money has to grow through the magic of compound interest. Compound interest is the interest earned on both your principal investment and the accumulated interest from previous periods.
This snowball effect significantly amplifies returns over time. For example, investing a small amount monthly at a young age will generate far more wealth than investing a larger sum later in life due to the extended compounding period.
This illustrates the importance of early investing in building long-term wealth. Time is your greatest asset when it comes to investing, and the younger you are, the more time you have to let your investments compound.
Higher Risk Tolerance and Long-Term Growth Potential
Young investors generally have a higher risk tolerance compared to older investors nearing retirement. This higher tolerance allows them to consider investments with higher growth potential, such as stocks, which historically have outperformed less risky options like bonds over the long term.
While these investments can experience greater volatility, the potential for substantial long-term returns outweighs the risks for those with a longer investment horizon.
The ability to weather market fluctuations is crucial for successful long-term investing, and youth offers the time needed to recover from temporary setbacks. This longer timeframe allows for riskier, potentially more rewarding investments.
This content may interest you! How to invest in your 50s in the UK?
How to invest in your 50s in the UK?Developing Financial Discipline and Planning Skills
Starting to invest early instills essential financial discipline and planning habits that benefit you far beyond just investment returns. The process of budgeting, researching investments, and monitoring your portfolio fosters responsibility and financial literacy.
These skills are invaluable in managing finances throughout life, regardless of your investment success. Learning to save and invest consistently at a young age sets a positive pattern for future financial decisions, leading to better overall financial health and a more secure future. The earlier you begin, the more ingrained these beneficial habits become.
| Advantage | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Compound Interest | Interest earned on both principal and accumulated interest, significantly increasing returns over time. |
| Time Horizon | Longer time allows for greater compounding and recovery from market downturns. |
| Risk Tolerance | Younger investors can take on more risk for potentially higher returns. |
| Financial Discipline | Investing early encourages responsible financial habits and planning. |
Is it smart to invest in stocks at a young age?
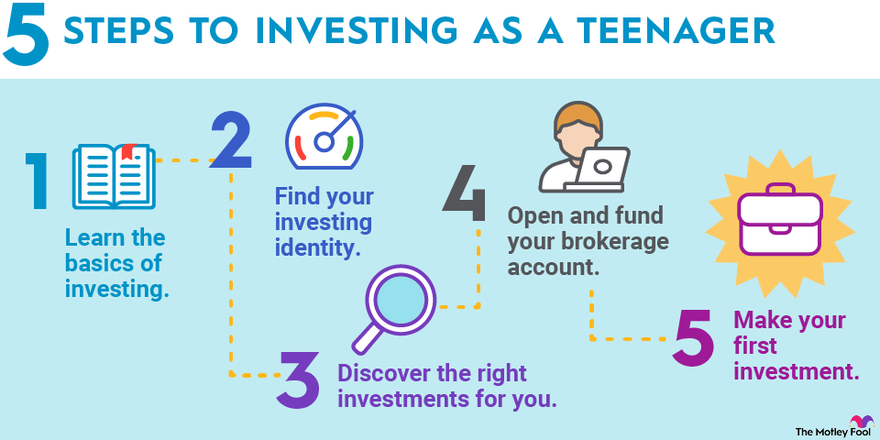
Investing in stocks at a young age can be a smart financial move, offering several significant advantages. The most crucial benefit is the power of compounding. Starting early allows your investments to grow exponentially over a longer period, leveraging the magic of compound interest.
Even small, consistent contributions made throughout your younger years can accumulate into a substantial sum by retirement. This long-term perspective mitigates the risk associated with short-term market fluctuations, as younger investors have more time to recover from potential downturns.
While there are inherent risks in stock market investing, the longer timeframe minimizes the impact of these risks. Furthermore, younger investors generally have more flexibility and time to adjust their investment strategies to adapt to changing market conditions. Finally, starting early fosters a valuable habit of saving and investing, which is crucial for long-term financial well-being.
Time Horizon and Risk Tolerance
A key aspect of investing in stocks at a young age is the extended time horizon. This longer timeframe allows investors to ride out market volatility, which is inevitable.
Younger investors typically have a higher risk tolerance, enabling them to allocate a larger portion of their portfolio to higher-growth, higher-risk assets like stocks. This approach can lead to significant gains over time. However, it's crucial to understand and accept that losses are possible, even likely, in the short term.
The extended time horizon offers the opportunity to recover from these losses and ultimately benefit from the market's long-term upward trend. This doesn't mean reckless investing, but a calculated approach that acknowledges the potential for both gains and losses.
- Longer time horizon reduces impact of short-term market fluctuations.
- Higher risk tolerance allows for investments in higher-growth assets.
- Understanding the potential for both gains and losses is crucial.
Diversification and Investment Strategies
Diversification is a crucial element of any successful investment strategy, and this is especially true for young investors. By spreading investments across various asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate, etc.) and sectors, young investors can reduce their overall risk.
This diversification can include investing in index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs), which offer broad market exposure. Furthermore, young investors can explore various investment strategies such as dollar-cost averaging, where they invest a fixed amount of money regularly, regardless of market conditions.
This helps mitigate the risk of investing a lump sum at a market peak. They can also adopt a long-term buy-and-hold strategy, focusing on holding investments for extended periods, rather than attempting to time the market.
This content may interest you! What should a 55 year old invest in?
What should a 55 year old invest in?- Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across different assets.
- Dollar-cost averaging helps mitigate the risk of market timing.
- Buy-and-hold strategy focuses on long-term growth, rather than short-term gains.
Education and Resources
Before starting any investment journey, especially in stocks, young investors should prioritize education. Understanding basic investment principles, risk management, and different investment vehicles is essential.
Fortunately, numerous resources are available to help, including online courses, books, financial advisors, and educational websites. Starting with a strong foundation of knowledge can significantly improve investment outcomes.
Learning about different investment strategies, asset allocation, and market analysis is crucial for making informed decisions. It's also important to understand the fees associated with different investment accounts and products to maximize returns.
Seeking guidance from a qualified financial advisor can be beneficial, especially when navigating complex investment choices.
- Education is crucial for understanding basic investment principles and risk management.
- Numerous online resources and financial advisors can provide valuable support.
- Understanding investment fees is key to maximizing returns.
Is it worth investing young?

Whether it's worth investing young depends heavily on individual circumstances, financial goals, and risk tolerance. However, generally speaking, starting to invest early offers significant advantages due to the power of compounding.
The longer your investments have to grow, the more time they have to generate returns, which are then reinvested to generate further returns. This snowball effect can lead to substantial wealth accumulation over time, even with relatively modest contributions. Early investing also allows for greater flexibility to adjust your investment strategy based on market fluctuations and life changes.
Conversely, younger investors may have less disposable income and more immediate financial priorities, such as paying off student loans or building an emergency fund. These competing demands might make it challenging to prioritize investing in the short term.
The key is to find a balance between present needs and long-term financial goals. A well-structured plan that accounts for both short-term and long-term needs is crucial. A financial advisor can help navigate this complex landscape and develop a tailored strategy.
The Power of Compounding
Compounding is the cornerstone of long-term investing success. It's the ability of your investments to generate returns, which are then reinvested to earn even more returns. The earlier you start, the longer your money has to compound, leading to exponentially larger returns over time.
This principle is especially beneficial for young investors who have decades ahead of them. It means that even small, regular contributions can grow into substantial sums over the long term.
This is due to the fact that not only is your initial investment growing, but the earnings on your initial investment are also growing.
This content may interest you! How much should a 50 year old have in savings UK?
How much should a 50 year old have in savings UK?- Early investing maximizes the impact of compounding, leading to significantly larger returns than investing later in life.
- Small, regular contributions made consistently over many years can accumulate to substantial wealth thanks to the power of compounding.
- Compounding growth allows your investment to grow at an increasing rate as your returns earn more returns over time.
Risk Tolerance and Time Horizon
Younger investors generally have a longer time horizon before they need to access their investments. This allows them to take on more risk in their investment strategy, potentially targeting higher-growth investments with a higher risk profile.
While there's always a chance of losses, the longer time horizon provides more opportunity to recover from any market downturns. A longer time horizon can also help reduce the emotional impact of market fluctuations, as there’s less pressure to sell investments at inopportune moments.
It's important to understand that a higher-growth investment may not be the right choice for every young investor. This depends on whether you are comfortable with the prospect of temporary losses.
- A longer time horizon allows for higher-risk investments to be considered, potentially yielding greater returns over the long term.
- Younger investors can benefit from riding out market downturns knowing they have more time for recovery.
- A longer time horizon reduces the emotional pressures that may tempt investors to make hasty decisions.
Balancing Immediate Needs and Long-Term Goals
While investing early is advantageous, it's crucial to balance long-term financial goals with immediate needs. Building an emergency fund is vital before aggressively investing. This provides a safety net for unexpected expenses, avoiding the need to liquidate investments at potentially unfavorable times.
Once an emergency fund is established, young investors can gradually increase their investment contributions as their income grows and their financial situation improves. This thoughtful approach allows for financial security in the present while maximizing the benefits of long-term investing.
- Prioritize building an emergency fund before committing significant funds to investments.
- Gradually increase investment contributions as income and financial stability improve.
- Carefully consider your immediate needs and financial obligations before focusing on long-term investment.
How much will $100 a month be worth in 30 years?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Clipboard03-df27c0eb3ccf470a9a424dbc0a13d93b.png)
The value of $100 a month in 30 years depends heavily on the rate of return you can achieve on your investments. There's no single answer, as investment returns are variable and uncertain. To illustrate, let's consider a few scenarios:
Scenario 1: A conservative estimate of 4% annual return (approximately the historical average for inflation-adjusted returns in the stock market). This assumes consistent investing and reinvestment of returns. We can use a future value of an ordinary annuity calculation:
FV = P [((1 + r)^n - 1) / r]
Where:
FV = Future Value
P = Periodic Payment ($100)
r = Rate of return per period (0.04/12 = 0.00333)
n = Number of periods (30 years 12 months = 360)
Plugging in the numbers, the future value is approximately $72,000. However, this does not account for taxes or fees. In reality, the actual value could be lower depending on investment performance and fees.
This content may interest you! Is saving $1000 a month good in the UK?
Is saving $1000 a month good in the UK?Scenario 2: A more optimistic scenario with an 8% annual return. Using the same formula, but with r = 0.08/12, the future value is approximately $175,000. This higher return implies a significantly greater final amount, but it also carries significantly greater risk.
Scenario 3: A pessimistic scenario with only 2% annual return (which could occur during periods of high inflation or low economic growth). Using the same formula, but with r = 0.02/12, the future value would be around $47,000. This highlights the importance of choosing appropriate investments to mitigate risk and achieve reasonable returns.
Factors Affecting Future Value
Several factors influence how much $100 a month invested today will be worth in 30 years. The most crucial is the rate of return. Higher returns lead to exponentially greater future values, but come with higher risk. Other considerations include inflation, which erodes the purchasing power of money over time, and the fees charged by investment platforms or financial advisors.
These fees can eat away at returns, reducing the overall final value. Finally, consistent investing is vital. Any interruptions in monthly contributions will negatively impact the final result.
- Rate of Return: This is the most significant factor. A higher rate leads to substantially greater growth.
- Inflation: Inflation decreases the purchasing power of your money. A high inflation rate diminishes the real value of your investment.
- Investment Fees: Fees charged by brokers, mutual funds, or advisors can significantly reduce your final returns. It's crucial to choose low-cost options.
Investment Strategies
The strategy you choose profoundly affects the final value. You could invest in stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or real estate. Each asset class offers a different risk-return profile. A diversified portfolio, which balances risk and reward by investing in a variety of asset classes, is often a wise approach.
Dollar-cost averaging, which involves investing a fixed amount at regular intervals regardless of market conditions, can help to mitigate the risk of investing a lump sum at a market high. Regular rebalancing of your portfolio can also help to maintain your desired level of risk and exposure to different assets.
- Diversification: Spreading your investments across different asset classes reduces risk.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: Investing regularly regardless of market fluctuations helps to manage risk.
- Rebalancing: Regularly adjusting your portfolio to maintain your target asset allocation.
Risk and Reward
Investing always involves some level of risk. Higher potential returns generally come with higher risk. Stocks, for instance, have historically provided higher returns than bonds but are also subject to greater price fluctuations. Understanding your risk tolerance is crucial before choosing an investment strategy. Consider your personal circumstances, financial goals, and time horizon.
A longer time horizon, such as 30 years, typically allows for greater risk-taking, as there is more time to recover from potential losses. However, it is still important to choose investments wisely to improve your chances of achieving your financial goals.
- Risk Tolerance: Assess your comfort level with potential investment losses.
- Time Horizon: A longer time horizon offers more opportunity to recover from losses.
- Investment Goals: Align your investments with your specific financial objectives.
Is investing in your 20s a good idea?

Yes, investing in your 20s is generally considered an excellent idea. This is primarily due to the power of compounding, which allows your investments to grow exponentially over time. The longer your money has to grow, the more significant the returns can be.
Starting early means you have decades for your investments to compound, leading to a much larger nest egg by retirement age compared to someone who starts later.
While there's risk involved in any investment, the potential rewards far outweigh the risks when starting young, given the extended timeframe available to recover from potential market downturns.
This content may interest you! What should your net worth be at 50 UK?
What should your net worth be at 50 UK?The Power of Compounding
The magic of compounding is arguably the most compelling reason to start investing in your twenties. Compounding refers to earning returns on your initial investment, and then earning returns on those returns.
This snowball effect significantly accelerates your investment growth over time. The earlier you start, the more time your money has to compound, leading to substantially higher returns compared to delaying your investments. Even small, consistent investments made early can grow into a substantial sum over several decades.
- Time horizon: A longer time horizon reduces the impact of short-term market fluctuations, allowing your investments to recover from downturns and experience significant long-term growth.
- Growth potential: Years of compounding returns exponentially increase your investment value, leading to a potentially large nest egg by retirement.
- Risk tolerance: A younger investor typically has a higher risk tolerance and a longer time horizon to recover from potential losses, making them better positioned to benefit from riskier but potentially higher-return investments.
Building Long-Term Financial Security
Investing in your 20s is a crucial step towards building long-term financial security. It allows you to proactively plan for major life events such as buying a home, starting a family, or funding your retirement.
Starting early helps to mitigate potential financial stress and provides a greater sense of financial stability throughout your life. The earlier you begin to save and invest, the less pressure you'll face in later life to catch up.
- Retirement planning: Investing early significantly increases your chances of achieving your retirement goals by allowing your investments to grow over a longer period.
- Major life purchases: Building a solid investment portfolio helps you finance significant life events such as buying a house or paying for your children's education.
- Financial independence: Consistent investing allows you to gradually achieve greater financial independence and security, reducing your reliance on external sources of income.
Overcoming the Fear of Investing
Many young adults hesitate to start investing due to fear of losing money. While it is important to be aware of the risks involved, it's equally crucial to remember that investing involves long-term planning, diversification, and risk management.
By starting small, educating yourself about different investment options, and considering consulting a financial advisor, you can significantly reduce your risk and build a healthy investment portfolio. Remember that consistent contributions, regardless of market fluctuations, are key to long-term success.
- Start small: Begin with small, manageable investments to gain experience and build confidence.
- Diversify your portfolio: Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce your risk.
- Seek professional advice: Consider consulting a financial advisor who can help you create a personalized investment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it too early to start investing in my twenties?
No, it's not too early! Starting young offers a significant advantage through the power of compounding. The earlier you begin, the longer your investments have to grow, benefiting from both market gains and the snowball effect of reinvesting profits.
Even small, regular contributions can accumulate substantially over decades. Don't let the perceived complexity deter you; many user-friendly platforms cater to beginners, making investing accessible and manageable regardless of your experience level. The sooner you start, the better positioned you'll be for long-term financial security.
What are the main benefits of investing young?
Investing young provides several key benefits. Firstly, you have a longer time horizon, allowing your investments to grow exponentially through compounding returns. Secondly, you can ride out market fluctuations more easily; younger investors have more time to recover from temporary downturns.
Thirdly, you'll likely have lower expenses and less financial responsibilities, making it easier to save and invest a larger portion of your income. Finally, consistent early investing cultivates discipline and financial literacy, laying the groundwork for future success in managing your finances effectively.
What if I don't have a lot of money to invest?
Even small amounts can make a significant difference when starting young. Many investment platforms allow for small, regular contributions, such as dollar-cost averaging, which mitigates the risk of investing a lump sum at an unfavorable market time.
Consider utilizing employer-sponsored retirement plans like 401(k)s, which often include employer matching contributions.
This content may interest you! What is the best investment for a small amount?
What is the best investment for a small amount?Focus on consistency over amount; regular investing, even with small sums, will yield better results over the long term than sporadic large investments. Explore low-cost index funds or ETFs for diversified growth.
What are some good investment options for young people?
Index funds and Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) offer diversified exposure to the market at low costs, making them suitable for beginners. Consider investing in broad market index funds that track the S&P 500 or a similar index to gain exposure to a wide range of companies.
Roth IRAs offer tax advantages for long-term growth, especially beneficial for younger investors expecting their tax bracket to increase in the future.
If you're risk-tolerant and have a longer time horizon, you might also consider allocating a small portion to higher-growth sectors, but always prioritize diversification to manage risk effectively.

Leave a Reply