How much is $1000 a month for 5 years?

Calculating the total value of a consistent monthly payment over an extended period is a fundamental financial skill. This article explores the simple yet crucial question: How much is $1000 a month for 5 years? We'll break down the calculation, illustrating the process step-by-step and offering practical applications.
Understanding this concept empowers you to make informed decisions regarding savings, investments, loan repayments, and budgeting, providing a clearer picture of your long-term financial outlook. Let's delve into the details.
How Much Does $1000 a Month Add Up To Over 5 Years?
Total Amount Received
If you receive $1000 per month for five years, the total amount you'll receive is calculated by multiplying the monthly amount by the number of months in five years.
There are 12 months in a year, and 5 years 12 months/year = 60 months. Therefore, $1000/month 60 months = $60,000. This is the total amount of money received over the five-year period without considering any interest or other factors.
Impact of Inflation
It's crucial to understand the impact of inflation. While $60,000 might seem like a significant sum, its purchasing power will decrease over five years due to inflation. Inflation erodes the value of money over time, meaning that $1000 today will likely buy less in five years.
The actual value of that $60,000 will be lower than its nominal value due to this erosion of purchasing power. To truly grasp the value, one would need to consider the predicted inflation rate over that period and adjust the final amount accordingly. This involves a process called discounting future cash flows.
Potential Investment Growth
Conversely, if this $1000 monthly income were invested, it could potentially grow beyond the simple $60,000 total. The actual amount would depend on the investment's rate of return.
For example, investing in a high-yield savings account or a diversified portfolio of stocks and bonds could generate interest or capital gains, resulting in a final amount significantly higher than $60,000. The specific return, however, is highly variable and depends on market conditions and investment choices.
This content may interest you! Is investing in your 20s a good idea?
Is investing in your 20s a good idea?| Scenario | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Total | $1000/month 60 months | $60,000 |
| Impact of Inflation (Example - 3% annual inflation) | Requires complex discounting calculations | Approximately $52,000 - $55,000 (Estimate) |
| Potential Investment Growth (Example - 7% annual return) | Requires complex compounding calculations | Approximately $70,000 - $75,000 (Estimate) |
How much to save a month to be a millionaire in 5 years?

To become a millionaire in 5 years requires saving $1,000,000 / 60 months (5 years x 12 months/year) = $16,666.67 per month. This calculation assumes no investment returns. Any investment earnings would reduce the amount needed to be saved monthly.
However, it's crucial to remember that achieving this goal depends heavily on consistent saving and potentially significant investment returns. This high monthly savings amount is challenging for most individuals and necessitates a high income or significant lifestyle changes.
Factors Affecting Monthly Savings
The required monthly savings to reach $1,000,000 in five years is significantly impacted by several factors. Ignoring these factors leads to inaccurate estimations.
Reaching this goal is a complex financial endeavor requiring a multifaceted approach.
- Investment returns: If your savings earn a consistent return (e.g., through investments in stocks, bonds, or real estate), the monthly savings requirement will be lower. The higher the return, the less you need to save each month.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money. A million dollars in five years will not have the same buying power as a million dollars today. To maintain the purchasing power of your goal, you'll need to adjust your savings target to account for inflation.
- Unexpected expenses: Life throws curveballs. Unexpected medical bills, car repairs, or job loss can significantly impact your savings progress. Building an emergency fund to cushion against unforeseen circumstances is critical for maintaining your saving plan.
Realistic Savings Strategies
Achieving a million dollars in savings within five years requires a strategic and disciplined approach. It's unrealistic for most individuals without already possessing substantial assets or a very high income. Consider a more gradual savings plan for a more attainable goal.
- Gradual accumulation: Instead of aiming for a million in five years, set a more realistic, longer-term goal. Smaller, incremental goals are more achievable and help to avoid burnout.
- Diversified investments: Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk and potentially increase returns. Consider consulting a financial advisor for personalized advice.
- Budgeting and expense tracking: Carefully track your expenses to identify areas where you can cut back and increase your savings rate. Creating a detailed budget is an essential step towards financial success.
Potential Risks and Challenges
Reaching such a significant savings goal in a short timeframe presents various risks and challenges. It's crucial to acknowledge these potential setbacks to avoid disappointment and build a more robust plan.
- Market volatility: Investment returns are not guaranteed. Market downturns can significantly impact your savings, potentially jeopardizing your goal. A well-diversified portfolio helps mitigate some of this risk.
- Unforeseen circumstances: Job loss, illness, or family emergencies can disrupt your savings plan. Having an emergency fund and contingency plans is essential to maintain financial stability.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Achieving such a high savings rate might require substantial lifestyle changes, which can be difficult to maintain over the long term. Finding a balance between saving and enjoying life is crucial.
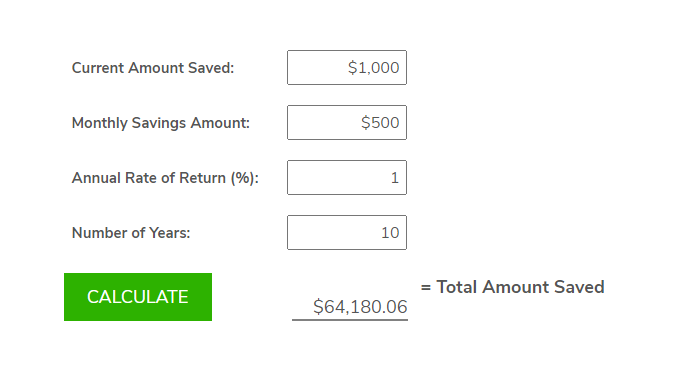
How much will I get if I save $1 000 a month for 10 years?
 What is the 70/30 rule in investing?
What is the 70/30 rule in investing?To calculate the final amount, we need to consider the effect of compound interest. The exact amount you'll have after 10 years depends entirely on the annual interest rate you earn on your savings. Let's explore a few scenarios:
Assuming an annual interest rate of 5%, compounded monthly, the formula to calculate the future value of an ordinary annuity is:
FV = P [((1 + r)^n - 1) / r]
Where:
FV = Future Value
P = Monthly payment ($1000)
r = Monthly interest rate (Annual interest rate / 12) = 0.05 / 12 = 0.004167
n = Number of months (10 years 12 months/year) = 120
Plugging in the values:
FV = $1000 [((1 + 0.004167)^120 - 1) / 0.004167]
FV ≈ $163,861.64
Therefore, with a 5% annual interest rate compounded monthly, you would have approximately $163,861.64 after 10 years. However, this is just an example. The actual amount will vary significantly depending on the interest rate.
This content may interest you! Can you start investing at a young age?
Can you start investing at a young age?Factors Affecting the Final Amount
Several factors influence the final amount accumulated from saving $1,000 per month for 10 years. The most significant factor is the interest rate earned on your savings. Higher interest rates lead to significantly larger returns due to the power of compounding.
Other factors include the frequency of compounding (monthly, quarterly, annually), and whether the interest is simple or compound. The more frequently the interest is compounded, the greater the final value.
- Interest Rate: The interest rate directly impacts the growth of your savings. A higher interest rate will result in a larger final sum.
- Compounding Frequency: The frequency with which interest is calculated and added to your principal affects the total. More frequent compounding (e.g., daily or monthly) yields higher returns than less frequent compounding (e.g., annually).
- Investment Type: The type of investment vehicle you choose (savings account, certificate of deposit, mutual fund, etc.) will impact the interest rate and the associated risks.
Calculating Future Value with Different Interest Rates
To illustrate how the interest rate affects your savings, let's consider different scenarios. If you earn a lower interest rate, such as 2%, your final amount will be significantly less. Conversely, a higher interest rate, for instance, 7%, will result in a considerably larger sum.
It's crucial to understand this relationship when making long-term savings plans.
- 2% Annual Interest: The future value would be significantly lower than the example above.
- 5% Annual Interest (as calculated above): This provides a good mid-range estimate.
- 7% Annual Interest: The future value would be considerably higher than the 5% example.
Importance of Consistent Savings and Early Investment
This example underscores the importance of consistent saving and early investment. Starting early allows your money to benefit from compounding for a longer period, leading to substantial growth.
Consistently contributing $1,000 per month for 10 years demonstrates dedication to financial goals and showcases the potential of disciplined savings.
- Long-Term Growth: The power of compounding is most effective over long periods.
- Financial Goals: Consistent saving facilitates achieving significant financial goals.
- Disciplined Savings: This example highlights the benefits of disciplined saving habits.
How much is $1000 a month for a year?
$1000 a month for a year is $12,000. This is calculated by multiplying the monthly amount ($1000) by the number of months in a year (12).
Calculating the Total Yearly Amount
To determine the total cost or income for the year, you simply multiply the monthly amount by the number of months. In this case, we have a monthly amount of $1000, and there are 12 months in a year.
This content may interest you! Is investing young smart?
Is investing young smart?Therefore, the calculation is as follows: $1000/month 12 months/year = $12,000/year. This simple calculation provides a straightforward answer to the question.
- Identify the monthly amount: $1000
- Identify the number of months in a year: 12
- Multiply the monthly amount by the number of months: $1000 12 = $12,000
Practical Applications of this Calculation
Understanding how to calculate yearly amounts from monthly figures has numerous practical applications. It's crucial for budgeting, financial planning, and assessing the overall cost or income of various financial commitments.
This calculation is essential for understanding annual expenses like rent, loan payments, subscriptions, or investment returns.
- Budgeting: Helps allocate funds effectively across the year.
- Financial Planning: Crucial for long-term savings and investment strategies.
- Assessing Costs: Enables accurate comparison of annual costs for different options.
Potential Variations and Considerations
While the basic calculation is straightforward, it's important to consider potential variations. For instance, if the monthly amount changes throughout the year, you'd need to calculate each month separately and sum the results.
Also, taxes, fees, or interest can impact the overall annual amount, adding further complexity to the calculation.
- Variable Monthly Amounts: Requires individual monthly calculations and summation.
- Additional Fees or Taxes: These add to the total annual cost, affecting the final figure.
- Interest Accrual: For investments, interest earned can significantly impact the final annual amount.
What is the $1000 a month rule for retirement calculator?

The "$1000 a month rule" isn't a formally established retirement calculation method like, for example, the 4% rule. Instead, it's a simplified guideline that suggests you need $12,000 a year ($1000 a month) in retirement income from various sources to maintain a basic standard of living.
This figure is highly subjective and varies greatly based on individual circumstances and location. It doesn't consider inflation, taxes, or unexpected expenses, making it a very rudimentary estimate. It essentially serves as a starting point for thinking about retirement income needs, prompting individuals to evaluate their savings and potential income streams against this benchmark.
This content may interest you! How to invest in your 50s in the UK?
How to invest in your 50s in the UK?This rule should not be considered a reliable financial planning tool on its own and should always be complemented by professional financial advice and more detailed retirement planning calculations.
What are the limitations of the $1000 a month rule?
The $1000 a month rule suffers from several significant limitations that render it unsuitable as a primary retirement planning tool. Its primary weakness lies in its simplicity, failing to account for several crucial factors.
Many unexpected events can drastically change retirement needs.
- Inflation: The purchasing power of $1000 today will be significantly lower in the future due to inflation. Failing to adjust for inflation leads to a considerable underestimation of retirement needs.
- Taxes: The $1000 is likely pre-tax income. The actual amount received after taxes will be less, impacting the real spending power.
- Unexpected Expenses: The rule doesn't account for unexpected medical expenses, home repairs, or other unforeseen events that can drain retirement savings.
How can the $1000 a month rule be used as a starting point for retirement planning?
While not a precise calculation, the $1000 a month rule can serve as a useful starting point for individuals to begin thinking about their retirement income needs. It can initiate conversations and help individuals begin to assess their financial situation.
- Assess Current Savings: Individuals can compare their current retirement savings against the target of $12,000 per year ($1000/month) to gauge their progress.
- Identify Income Sources: The rule highlights the need to diversify income sources in retirement, such as Social Security, pensions, and investments.
- Adjust for Individual Circumstances: The $1000 a month figure should be personalized based on individual lifestyle and location, considering cost of living and desired lifestyle.
What alternative retirement planning tools are available?
More comprehensive retirement planning tools should be used in addition to or instead of the $1000 a month rule. These tools offer a much more nuanced and accurate projection of retirement needs.
- Retirement Calculators: Online and financial advisor retirement calculators incorporate factors like inflation, taxes, and investment returns to project future retirement income needs.
- Financial Advisors: Consulting a financial advisor provides personalized guidance and a more tailored retirement plan based on individual circumstances and financial goals.
- The 4% Rule: A more sophisticated rule of thumb suggesting withdrawing 4% of your retirement savings annually, adjusting for inflation. Even this rule, however, has limitations and requires careful consideration.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much is $1000 a month for 5 years in total?
To calculate the total amount, you simply multiply the monthly payment by the number of months in five years. There are 12 months in a year, so 5 years equals 60 months (5 years 12 months/year = 60 months). Therefore, $1000/month 60 months = $60,000.
So, $1000 a month for 5 years totals $60,000. This calculation doesn't account for interest, which would be relevant if this was a loan payment scenario. It's a simple calculation useful for budgeting or understanding the overall cost of a consistent monthly expense.
What if I want to calculate this for a different time period?
The calculation is easily adaptable. Simply determine the total number of months in your desired time period and multiply that by the monthly amount. For example, if you wanted to know the total for 3 years, you'd calculate 3 years 12 months/year = 36 months. Then multiply $1000/month by 36 months to get a total of $36,000. The formula is always (Number of years 12 months/year) Monthly payment.
This content may interest you! How to make $5,000 a month fast?
How to make $5,000 a month fast?Remember this calculation doesn't factor in any interest or other potential costs that might be associated with the payment.
How can I use this calculation for budgeting purposes?
This calculation is extremely helpful for budgeting. Knowing that a $1000 monthly expense will cost $60,000 over 5 years allows you to accurately allocate funds and create a realistic budget.
This helps in planning for major expenses, saving for large purchases, or understanding the long-term financial impact of a recurring cost like rent, loan payments, or even investments. You can use this to plan ahead and avoid unexpected financial strain by accounting for the total cumulative cost over the specified time frame.
Does this calculation include interest?
No, this calculation is strictly based on the simple multiplication of the monthly payment and the total number of months. It does not take into account any interest that might accrue, which is crucial when dealing with loans or investments.
Interest significantly alters the total amount paid or earned over time. To calculate the total cost with interest, you'd need to use a more complex formula that considers the interest rate and compounding periods. This basic calculation is suitable only for understanding the total amount of principal paid without any additional interest.

Leave a Reply