What is the 70 20 10 budget rule?

The 70 20 10 budget rule is a simple yet effective financial strategy designed to help individuals manage their income efficiently. This rule divides your after-tax income into three categories: 70% for living expenses, 20% for savings and debt repayment, and 10% for investments or charitable contributions. By allocating funds in this structured manner, the rule promotes financial stability, encourages disciplined spending, and fosters long-term wealth-building habits. Whether you're new to budgeting or seeking a more streamlined approach to managing your finances, the 70 20 10 rule offers a practical framework to achieve your financial goals while maintaining balance in your daily life.
What is the 70 20 10 Budget Rule?
The 70 20 10 budget rule is a simple and effective method for managing personal finances. It suggests dividing your after-tax income into three categories: 70% for living expenses, 20% for savings and investments, and 10% for debt repayment or charitable contributions. This approach helps individuals prioritize their spending, build savings, and reduce debt systematically. It’s particularly useful for those who want a straightforward framework to achieve financial stability without complex calculations.
How Does the 70 20 10 Budget Rule Work?
The 70 20 10 budget rule works by allocating your income into three distinct categories. First, 70% of your income is dedicated to covering essential living expenses, such as rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation. Next, 20% is set aside for savings and investments, which can include emergency funds, retirement accounts, or other financial goals. Finally, 10% is used for debt repayment (like credit cards or loans) or charitable donations. This structure ensures a balanced approach to managing money while promoting long-term financial health.
Benefits of Using the 70 20 10 Budget Rule
One of the main benefits of the 70 20 10 budget rule is its simplicity. It provides a clear framework for managing finances without requiring detailed tracking of every expense. Additionally, it encourages financial discipline by prioritizing savings and debt repayment. By allocating 20% to savings, individuals can build an emergency fund or invest for the future, while the 10% for debt repayment helps reduce financial burdens over time. This rule is especially helpful for those who struggle with overspending or lack a structured budgeting plan.
This content may interest you! What is the 50/20/30 budget rule?
What is the 50/20/30 budget rule?Who Should Use the 70 20 10 Budget Rule?
The 70 20 10 budget rule is ideal for individuals who prefer a straightforward and flexible budgeting method. It’s particularly suitable for those with stable incomes and moderate living expenses. However, it may require adjustments for people with high debt levels or those living in areas with high costs of living. If you’re someone who values simplicity and wants to balance spending, saving, and debt repayment, this rule can be an excellent starting point for achieving your financial goals.
| Category | Percentage | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Living Expenses | 70% | Cover essential needs like rent, utilities, and groceries. |
| Savings & Investments | 20% | Build emergency funds, retirement savings, or other financial goals. |
| Debt Repayment/Charity | 10% | Pay off debts or contribute to charitable causes. |
What is the 70/20/10 budget rule example?

Understanding the 70/20/10 Budget Rule
The 70/20/10 budget rule is a simple and effective way to manage your finances by dividing your after-tax income into three categories: needs, savings, and wants. Here’s how it works:
- 70% of your income is allocated to needs, such as rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation.
- 20% of your income is dedicated to savings, including emergency funds, retirement accounts, and debt repayment.
- 10% of your income is reserved for wants, such as dining out, entertainment, and non-essential purchases.
Applying the 70/20/10 Budget Rule to Your Finances
To implement the 70/20/10 budget rule, follow these steps:
This content may interest you! What is the 60/20/20 budget rule?
What is the 60/20/20 budget rule?- Calculate your after-tax income to determine the total amount available for budgeting.
- Allocate 70% of your income to cover essential expenses, ensuring that your basic needs are met.
- Set aside 20% of your income for savings and financial goals, such as building an emergency fund or paying off debt.
- Use the remaining 10% for discretionary spending, allowing yourself some flexibility for leisure and personal enjoyment.
Benefits of the 70/20/10 Budget Rule
The 70/20/10 budget rule offers several advantages for managing your finances effectively:
- It provides a clear structure for allocating your income, making it easier to track spending and savings.
- It encourages financial discipline by prioritizing needs and savings over discretionary spending.
- It allows for flexibility in your budget, ensuring that you can enjoy some of your income while still meeting financial goals.
What is better than the 50/30/20 rule?

The 70/20/10 Budgeting Rule
The 70/20/10 rule is an alternative to the 50/30/20 rule, offering a more aggressive approach to saving and investing. This method allocates:
- 70% of your income to living expenses, including necessities and discretionary spending.
- 20% to savings, which can include emergency funds, retirement accounts, or other long-term goals.
- 10% to investments or debt repayment, focusing on building wealth or reducing liabilities.
This rule is ideal for individuals who prioritize financial growth and are comfortable with a tighter budget for discretionary spending.
This content may interest you! What is the 40-40-20 budget rule?
What is the 40-40-20 budget rule?The Zero-Based Budgeting Method
Zero-based budgeting is a more detailed and proactive approach compared to the 50/30/20 rule. It involves:
- Assigning every dollar of your income to a specific category, ensuring no money is left unallocated.
- Tracking expenses meticulously to ensure you stay within your budget limits.
- Adjusting your budget monthly to reflect changes in income, expenses, or financial goals.
This method is particularly effective for those who want full control over their finances and are willing to invest time in planning and tracking.
The 60/20/20 Budgeting Rule
The 60/20/20 rule is another alternative that emphasizes saving and debt repayment. It divides your income as follows:
- 60% for fixed expenses, such as rent, utilities, and groceries.
- 20% for financial goals, including savings, investments, or paying off debt.
- 20% for flexible spending, such as entertainment, dining out, or hobbies.
This rule is suitable for individuals who want a balanced approach, allowing for both financial security and personal enjoyment.
This content may interest you! How to save money from a young age?
How to save money from a young age?What is 50 30 20 budget rule stands for?

Understanding the 50 30 20 Budget Rule
The 50 30 20 budget rule is a simple and effective method for managing personal finances. It divides your after-tax income into three main categories:
- 50% for Needs: This portion of your income should cover essential expenses such as housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and insurance.
- 30% for Wants: This category includes discretionary spending on non-essential items like dining out, entertainment, hobbies, and vacations.
- 20% for Savings and Debt Repayment: This part of your income should be allocated to building an emergency fund, saving for retirement, or paying off debts.
Benefits of the 50 30 20 Budget Rule
Adopting the 50 30 20 budget rule offers several advantages for financial management:
- Simplicity: The rule is easy to understand and implement, making it accessible for individuals at any financial level.
- Flexibility: It allows for adjustments based on personal circumstances, ensuring it can adapt to different lifestyles and income levels.
- Balance: By dividing income into needs, wants, and savings, it promotes a balanced approach to spending and saving, helping to avoid overspending in any one category.
How to Implement the 50 30 20 Budget Rule
To effectively use the 50 30 20 budget rule, follow these steps:
This content may interest you! How to budget as a young person?
How to budget as a young person?- Calculate Your After-Tax Income: Determine your monthly income after taxes and deductions to establish your budget baseline.
- Categorize Your Expenses: Divide your expenses into needs, wants, and savings/debt repayment based on the 50 30 20 percentages.
- Track and Adjust: Regularly monitor your spending to ensure you stay within the allocated percentages and make adjustments as needed to maintain financial stability.
Is the 70/20/10 rule good?
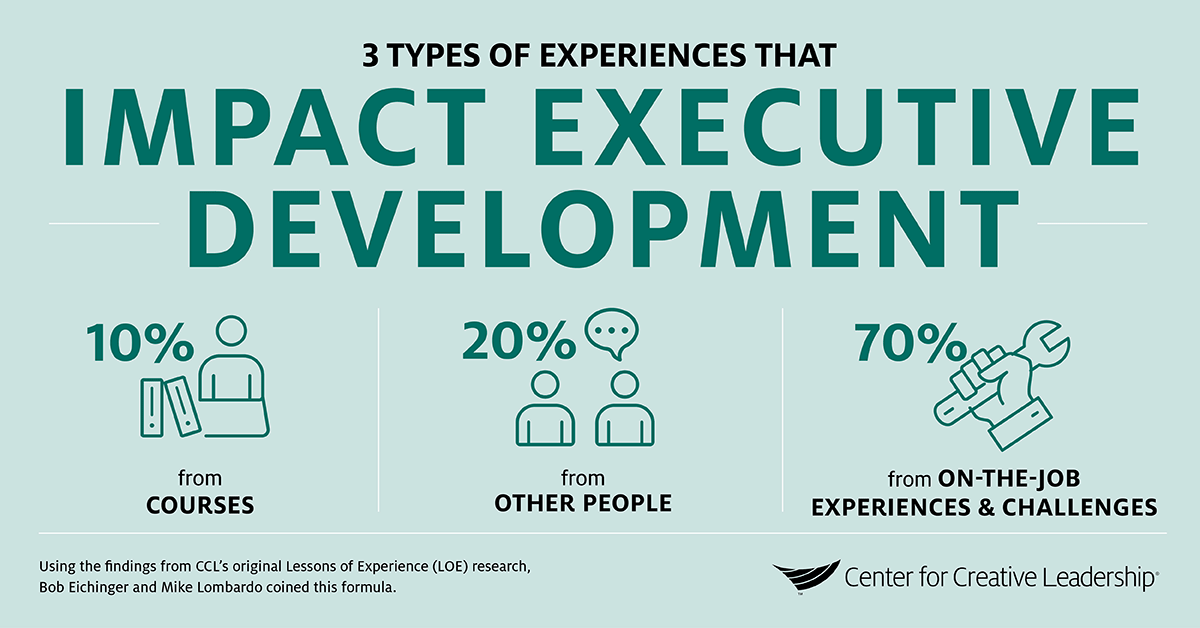
What is the 70/20/10 Rule?
The 70/20/10 rule is a learning and development model that suggests a balanced approach to professional growth. It proposes that:
- 70% of learning comes from on-the-job experiences, such as tackling real-world challenges and tasks.
- 20% of learning is derived from social interactions, including feedback, mentoring, and collaboration with peers.
- 10% of learning is acquired through formal education, such as courses, workshops, and training programs.
Advantages of the 70/20/10 Rule
The 70/20/10 rule offers several benefits for both individuals and organizations:
- It emphasizes practical, hands-on learning, which can lead to faster skill acquisition and better retention.
- It encourages collaboration and networking, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and knowledge sharing.
- It provides a structured yet flexible framework for professional development, allowing individuals to tailor their learning experiences.
Limitations of the 70/20/10 Rule
While the 70/20/10 rule has its merits, it also has some limitations:
This content may interest you! What is the 70-10-10-10 budget rule?
What is the 70-10-10-10 budget rule?- It may not suit all industries or roles, as some professions require a heavier emphasis on formal education or certifications.
- The model assumes that employees have access to meaningful on-the-job experiences and supportive social interactions, which may not always be the case.
- It can be challenging to measure the effectiveness of the 70/20/10 approach, as learning outcomes are often subjective and context-dependent.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the 70 20 10 budget rule?
The 70 20 10 budget rule is a simple money management strategy where you allocate 70% of your income to living expenses, 20% to savings or debt repayment, and 10% to investments or charitable donations. It helps individuals prioritize spending, build savings, and plan for the future while maintaining financial balance.
How does the 70 20 10 budget rule work?
The rule works by dividing your after-tax income into three categories: 70% for necessities like rent, utilities, and groceries, 20% for savings or paying off debt, and 10% for investments or donations. This structure ensures you cover essential expenses, build financial security, and allocate funds for long-term growth or giving back.
Who should use the 70 20 10 budget rule?
The 70 20 10 budget rule is ideal for individuals seeking a straightforward budgeting method. It works well for those with stable incomes who want to balance spending, saving, and investing. However, it may need adjustments for people with irregular income or high debt levels to better suit their financial situation.
What are the benefits of the 70 20 10 budget rule?
The 70 20 10 budget rule offers simplicity, flexibility, and a clear framework for managing finances. It encourages disciplined spending, helps build savings, and promotes long-term financial growth through investments. By allocating funds intentionally, it reduces stress and ensures a balanced approach to money management.
This content may interest you! What is the 50/30/20 rule of money?
What is the 50/30/20 rule of money?https://youtube.com/watch?v=KcEIkJQZHr4

Leave a Reply