What is the 70 saving rule?

The 70 saving rule is a straightforward budgeting strategy designed to help individuals manage their finances effectively. This rule suggests allocating 70% of your income towards essential and discretionary expenses, while the remaining 30% is dedicated to savings and investments.
By following this approach, you can maintain a balanced financial lifestyle, ensuring that your immediate needs are met while also building a secure future.
The rule emphasizes the importance of disciplined spending and consistent saving, making it an accessible method for those looking to improve their financial health. Whether you're new to budgeting or seeking a simpler framework, the 70 saving rule offers a practical solution.
What is the 70 Saving Rule?
The 70 Saving Rule is a budgeting guideline that suggests allocating 70% of your income for monthly expenses, while the remaining 30% is divided between savings and investments. This rule is designed to help individuals maintain a balanced financial lifestyle, ensuring that they can cover their needs while still building wealth for the future.
This content may interest you! What is the 80/20 rule in saving money?
What is the 80/20 rule in saving money?It is particularly useful for those who want a simple and effective way to manage their finances without overly complicated budgeting methods.
How Does the 70 Saving Rule Work?
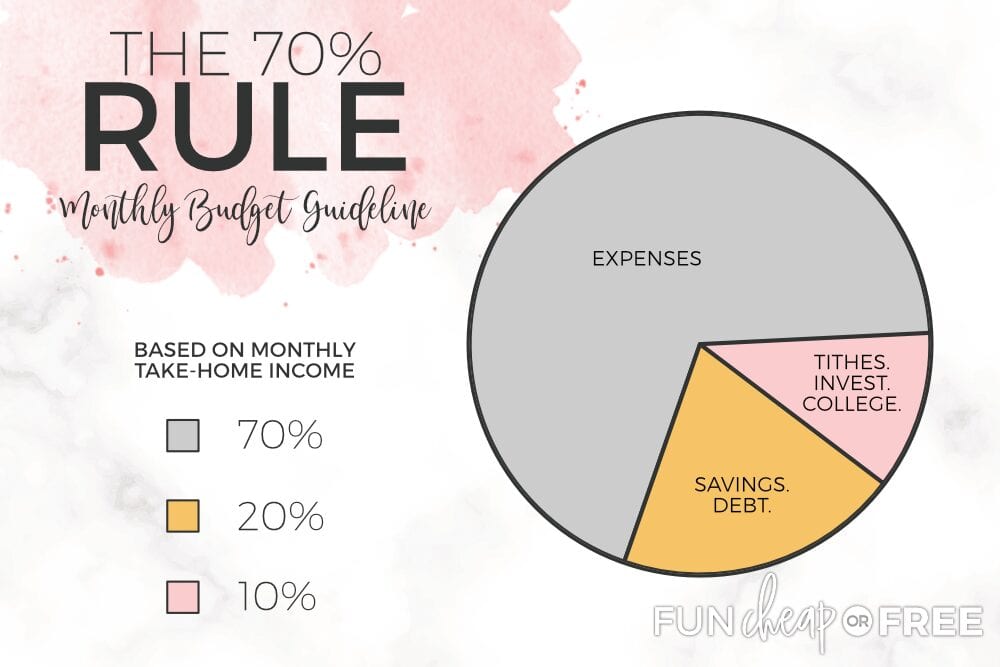
The 70 Saving Rule works by dividing your after-tax income into three main categories. 70% is allocated to cover all your monthly expenses, such as rent, utilities, groceries, and entertainment. The remaining 30% is split between savings (20%) and investments (10%).
This structure ensures that you prioritize your immediate needs while still setting aside funds for future financial security and growth.
Benefits of Using the 70 Saving Rule
One of the key benefits of the 70 Saving Rule is its simplicity. It provides a clear framework for managing your finances without requiring detailed tracking of every expense. Additionally, it encourages consistent saving and investing, which can lead to long-term financial stability.
This content may interest you! What is the 60 saving rule?
What is the 60 saving rule?By sticking to this rule, you can avoid overspending and ensure that you are building a financial cushion for emergencies or future goals.
Who Should Use the 70 Saving Rule?
The 70 Saving Rule is ideal for individuals who prefer a straightforward budgeting approach and want to avoid the complexity of more detailed financial plans. It is especially useful for young professionals or those with a steady income who are looking to balance their current lifestyle with future financial goals.
However, it may require adjustments for those with irregular incomes or significant debt obligations.
| Category | Percentage | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Expenses | 70% | Covers essential and discretionary spending |
| Savings | 20% | Builds an emergency fund or saves for future goals |
| Investments | 10% | Grows wealth over time through investments |
What is the 70% income rule?
 Can I retire at 60 with 300k?
Can I retire at 60 with 300k?Understanding the 70% Income Rule
The 70% income rule is a budgeting guideline that suggests allocating 70% of your gross income to cover all living expenses. This includes necessities such as housing, utilities, groceries, transportation, and other recurring costs.
The remaining 30% is typically divided between savings, investments, and discretionary spending. The rule aims to create a balanced financial plan that ensures essential needs are met while also promoting financial growth and flexibility.
- 70% of income is dedicated to essential living expenses.
- The remaining 30% is split between savings, investments, and discretionary spending.
- This rule helps maintain a balance between current needs and future financial goals.
How to Apply the 70% Income Rule
To implement the 70% income rule, start by calculating your total gross income. Then, allocate 70% of this amount to cover your essential expenses. This includes fixed costs like rent or mortgage payments, utilities, insurance, and variable expenses such as groceries and transportation.
The remaining 30% should be divided into savings (10-15%), investments (10-15%), and discretionary spending (5-10%). This approach ensures that you are living within your means while also building a financial cushion for the future.
This content may interest you! How many people have $1,000,000 in retirement savings?
How many people have $1,000,000 in retirement savings?- Calculate your gross income and allocate 70% to essential expenses.
- Divide the remaining 30% into savings, investments, and discretionary spending.
- Regularly review and adjust your budget to stay on track.
Benefits of the 70% Income Rule
The 70% income rule offers several advantages for financial planning. It provides a clear framework for managing income, ensuring that essential needs are prioritized. By allocating a portion of income to savings and investments, it encourages long-term financial stability and growth.
Additionally, the rule allows for some discretionary spending, which can improve quality of life without compromising financial health. This balanced approach helps individuals avoid overspending and reduces the risk of financial stress.
- Prioritizes essential expenses while promoting financial growth.
- Encourages disciplined saving and investing habits.
- Provides flexibility for discretionary spending without compromising financial stability.
Is 50/30/20 or 70/20/10 better?

Understanding the 50/30/20 Budget Rule
The 50/30/20 budget rule is a popular method for managing personal finances. It divides your after-tax income into three categories:
This content may interest you! Can you have savings if you have debt?
Can you have savings if you have debt?- 50% for needs: This includes essential expenses like rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation.
- 30% for wants: This covers non-essential spending such as dining out, entertainment, and hobbies.
- 20% for savings and debt repayment: This portion is allocated to building an emergency fund, saving for retirement, or paying off debt.
Exploring the 70/20/10 Budget Rule
The 70/20/10 budget rule is another approach to managing finances, with a different allocation of income:
- 70% for living expenses: This includes both needs and wants, such as housing, food, entertainment, and other discretionary spending.
- 20% for savings: This portion is dedicated to long-term savings goals, such as retirement or investments.
- 10% for debt repayment or charitable giving: This smaller percentage is used to pay off debt or donate to causes you care about.
Comparing 50/30/20 and 70/20/10 Budget Rules
When deciding between the 50/30/20 and 70/20/10 budget rules, consider the following factors:
- Flexibility: The 50/30/20 rule provides a clear separation between needs and wants, while the 70/20/10 rule combines them, offering more flexibility in discretionary spending.
- Savings focus: The 50/30/20 rule allocates a larger percentage (20%) to savings and debt repayment, making it ideal for those prioritizing financial security. The 70/20/10 rule focuses more on living expenses, with a smaller portion (20%) for savings.
- Debt management: If you have significant debt, the 50/30/20 rule may be more effective, as it dedicates a larger portion of your income to debt repayment. The 70/20/10 rule allocates only 10% to debt, which may not be sufficient for those with high debt levels.
What is the 40 30 20 10 rule?

Understanding the 40 30 20 10 Rule
The 40 30 20 10 rule is a budgeting framework designed to help individuals allocate their income effectively. It divides your income into four categories: 40% for necessities, 30% for discretionary spending, 20% for savings, and 10% for investments or debt repayment. This rule provides a structured approach to managing finances while ensuring a balance between immediate needs and long-term goals.
This content may interest you! What is the 60/20/20 budget rule?
What is the 60/20/20 budget rule?- 40% of your income is allocated to necessities such as rent, utilities, groceries, and transportation.
- 30% is designated for discretionary spending, which includes entertainment, dining out, and hobbies.
- 20% is set aside for savings, including emergency funds and retirement accounts.
- 10% is used for investments or paying off debts, helping to build wealth over time.
Benefits of the 40 30 20 10 Rule
The 40 30 20 10 rule offers several advantages for financial planning. It simplifies budgeting by providing clear percentages for different spending categories, making it easier to track and manage expenses. Additionally, it encourages disciplined saving and investing, which are crucial for long-term financial stability.
- It promotes financial discipline by setting clear limits on spending categories.
- It ensures that essential needs are prioritized while still allowing room for enjoyment.
- It fosters a habit of saving and investing, which can lead to financial growth over time.
How to Implement the 40 30 20 10 Rule
Implementing the 40 30 20 10 rule requires careful planning and consistent tracking of your income and expenses. Start by calculating your total monthly income and then divide it according to the rule's percentages. Use budgeting tools or apps to monitor your spending and make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
- Calculate your total monthly income after taxes and deductions.
- Allocate 40% to necessities, 30% to discretionary spending, 20% to savings, and 10% to investments or debt repayment.
- Use budgeting tools or apps to track your spending and ensure you adhere to the allocated percentages.
How to calculate 70% of your income?

Understanding the Basics of Income Calculation
To calculate 70% of your income, you first need to determine your total income. This includes all sources of revenue, such as salary, bonuses, freelance work, and any other earnings. Once you have your total income, you can proceed to calculate 70% of it.
This content may interest you! What is the 50/20/30 budget rule?
What is the 50/20/30 budget rule?- Identify all sources of income.
- Sum up the total amount from these sources.
- Multiply the total income by 0.70 to find 70% of your income.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating 70% of Your Income
Calculating 70% of your income involves a straightforward mathematical process. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide to help you through it:
- List all your income sources, including your salary, bonuses, and any other earnings.
- Add up all these amounts to get your total income.
- Multiply the total income by 0.70. This will give you 70% of your income.
Practical Applications of Calculating 70% of Your Income
Understanding how to calculate 70% of your income can be useful in various financial planning scenarios. Here are some practical applications:
- Budgeting: Allocate 70% of your income to essential expenses like rent, utilities, and groceries.
- Savings: Use 70% of your income to determine how much you can save or invest each month.
- Debt Repayment: Calculate 70% of your income to plan for debt repayment strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the 70 saving rule?
The 70 saving rule is a budgeting guideline that suggests allocating 70% of your income to essential and discretionary expenses, while saving or investing the remaining 30%. This rule helps individuals prioritize financial growth while maintaining a balanced lifestyle.
How does the 70 saving rule work?
The 70 saving rule works by dividing your income into two categories: 70% for living expenses, such as housing, food, and entertainment, and 30% for savings, investments, or debt repayment. This approach ensures consistent financial progress without compromising daily needs.
Who should use the 70 saving rule?
The 70 saving rule is ideal for individuals seeking a simple and effective way to manage their finances. It suits those with stable incomes who want to balance spending and saving without detailed budgeting.
What are the benefits of the 70 saving rule?
The 70 saving rule promotes financial discipline, encourages consistent savings, and simplifies budgeting. It allows flexibility in spending while ensuring a portion of income is dedicated to future financial security or goals.

Leave a Reply